Conformalized Forecasting using Machine Learning (and statistical) models with ARCH effects
mlarchf.RdConformalized Forecasting using Machine Learning (and statistical) models with ARCH effects
mlarchf(
y,
h = 10L,
mean_model = forecast::auto.arima,
model_residuals = forecast::meanf,
fit_func = ahead::ridge,
predict_func = predict,
lags_vol = 10L,
type_pi = c("surrogate", "bootstrap", "kde"),
type_sim_conformalize = c("surrogate", "block-bootstrap", "bootstrap", "kde",
"fitdistr"),
ml_method = NULL,
level = 95,
B = 250L,
ml = TRUE,
stat_model = NULL,
n_clusters = 0,
clustering_dist = "euclidean",
clustering_method = "kmeans",
...
)Arguments
- y
A numeric vector or time series of class
ts- h
Forecasting horizon
- mean_model
Function to fit the mean model (default:
forecast::auto.arima)- model_residuals
Function to model the residuals (default:
forecast::thetaf)- fit_func
Fitting function for the variance model (default:
ahead::ridge)- predict_func
Prediction function for the variance model (default:
predict)- lags_vol
Number of lags for squared residuals regression
- type_pi
Type of prediction interval ("kde", "surrogate", or "bootstrap") for volatility modeling
- type_sim_conformalize
Type of simulation for conformalization of standardized residuals ("block-bootstrap", "surrogate", "kde", "bootstrap", or "fitdistr")
- ml_method
caret package Machine learning method to use, if
fit_funcandpredict_funcaren't provided. If NULL, usesfit_funcandpredict_func. Seeunique(caret::modelLookup()$model).- level
Confidence level for prediction intervals
- B
Number of bootstrap replications or simulations
- ml
If
TRUE,fit_funcandpredict_funcare used, otherwise a statistical model instat_model- stat_model
A statistical model, e.g
forecast::thetaforforecast::auto.arima- n_clusters
Number of clusters for residuals (default is 0) for
ml == TRUEandml_methodnotNULL- clustering_dist
Only if
n_clusters > 0. If "euclidean", then mean square error, if "manhattan ", the mean absolute error is used.- clustering_method
Only if
n_clusters > 0. If "kmeans", then we have the kmeans clustering method, if "hardcl" we have the On-line Update (Hard Competitive learning) method, and if "neuralgas", we have the Neural Gas (Soft Competitive learning) method. Abbreviations of the method names are accepted.- ...
Additional parameters to be passed to
stat_model
Value
A forecast object containing predictions and prediction intervals
Examples
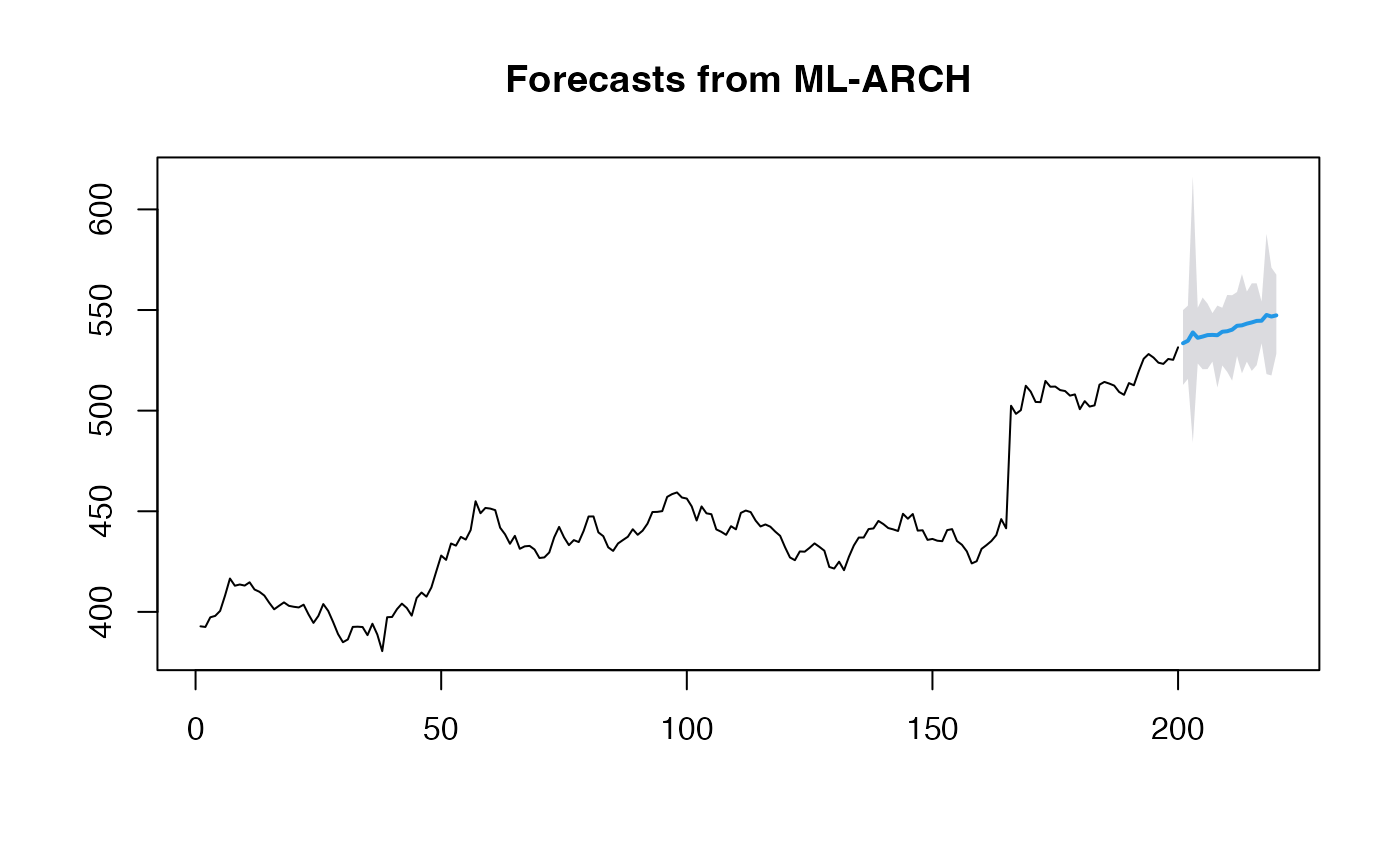
y <- fpp2::goog200
# Default model for volatility (Ridge regression for volatility)
(obj_ridge <- ahead::mlarchf(y, h=20L, B=500L))
#> Point Forecast Lo 95 Hi 95
#> 201 534.4214 513.0126 549.3933
#> 202 536.2434 516.2732 554.8150
#> 203 536.4303 521.4628 553.5272
#> 204 536.6375 516.4954 559.5297
#> 205 536.9744 513.3218 555.6087
#> 206 536.8669 518.1739 552.4974
#> 207 539.0674 519.1329 558.1132
#> 208 537.4618 501.6436 560.6395
#> 209 540.1076 518.9179 558.1104
#> 210 536.5789 509.1344 555.3092
#> 211 540.7064 517.4373 555.1692
#> 212 543.6837 528.5274 561.0367
#> 213 543.4614 524.3126 564.4024
#> 214 544.3046 526.8852 564.2636
#> 215 544.1797 522.0492 560.9355
#> 216 544.7224 525.9826 560.9314
#> 217 545.7186 524.2705 564.2966
#> 218 546.5558 524.4960 568.5002
#> 219 546.0634 527.0138 562.9881
#> 220 548.5014 525.1081 567.3897
plot(obj_ridge)